
1. X-rays have uses beyond diagnostic imaging.
In addition to their amazing uses in the medical field, x-rays have been used in the art world to examine under-paintings, which are rough sketches artists used to guide their final paintings. They have also been used to examine priceless artifacts, such as ancient Egyptian mummies or amber fossils, more closely without damaging them. X-rays have even been launched into space to gain glimpses into space far beyond our solar system.
2. Wilhelm Roentgen Did Not Patent the X-Rays

Wilhelm Roentgen did not patent the X-ray. He did not want the use of X-rays to be limited for patients. Roentgen saw the value of his invention and wanted everyone to benefit not just doctors and scientists. Overall the use of x-rays is more widely used for different treatments and more affordable to patients because of him.
3. Difference between “soft” and “hard” X-rays.
Doctors and scientists use hard X-rays to look at broken bones or investigate solid materials’ atomic-level properties. Soft X-rays carry far less energy than hard X-rays and are more easily absorbed by air and other mediums. In water, most soft X-ray photons will be absorbed before they have travelled even a millionth of a meter.
4. X-rays were used to discover the double helical structure of DNA.
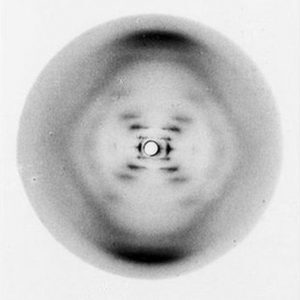
Although James Watson and Francis Crick are typically credited with the discovery of the structure of DNA, their breakthrough would not have been possible without the X-ray crystallography performed by chemist Rosalind Franklin. X-ray crystallography involves striking a crystal’s surface with X-rays and then looking at the “scattering” pattern generated. By working backwards mathematically, scientists can reconstruct the structure of small molecules from these intricate patterns.
5. Brightest Ever X-ray Shows Lung Vessels Altered by COVID-19

Scientists at the University College London in the U.K. and the European Synchrotron Research Facility in France used a machine called Hierarchical Phase-Contrast Tomography (HiP-CT), the brightest X-ray in the world to scan donated human organs, including lungs, from a donor who had COVID-19.
HiP-CT allows researchers and scientists to utilize 3D mapping of the object scanned at various scales by imaging the whole organ and then zooming down to a cellular level, according to a release. Due to this intense brilliance, researchers can view blood vessels five microns in diameter (a tenth of the diameter of a hair) in an intact human lung. A clinical CT scan only resolves blood vessels that are about 100 times larger, around 1mm in diameter.
CONTACT US FOR YOUR RADIOGRAPHY TESTING
Radiographic testing is a positive approach for finding porosity, cracks, inclusions and voids inside weldments. The dimensions and angles within the sample can be measured without sectioning. In this way, surface and subsurface defects can be uncovered via this method.
In PTS, our radiography testing team will place your metal test sample in between the radiation source and a sensitive film. The metal absorbs or scatters away some of the radiation, and reduces the amount of radiation reaching the film. This results in a lighter shade of gray, once the film is developed. However, if there is a change in either the amount of metal or the type of material at a specific location on a sample, the amount of radiation absorbed or scattered changes as well.
Air, as a trapped bubble or pore, reduces the amount of metal present, increases the radiation reaching the film, and results in a circular mark on the film, in a darker shade of gray than the image of the surrounding metal. Additional metal, such as due to excess weld reinforcement or due to a design feature, will increase the amount of metal, decreasing the radiation reaching the film, and results in a 2D topographical image of the feature on the film, in a lighter shade of gray than the image of the surrounding metal. Likewise, the presence of dense materials such as copper, lead or tungsten in the sample, will also decrease radiation and an image that is lighter than the surrounding area on the film.










