Reveal a Material’s 3-Dimensional Insides
with 3D X-ray Computed Tomography
3D X-ray computed tomography (also known as 3D micro computed tomography or micro CT) is one of the advanced non-destructive testing (NDT) computed tomography methods. It visualises interior features within a test sample and obtains high-density information on their 3D geometries, structures, defects, material density variations and internal components.
When X-rays are projected through and around a sample, they form a ‘shadow’ of the attenuated specimen, or X-ray image, on a digital detector. This method is beneficial for checking for underlying indications such as cracks, pores, or inclusions. This technique requires thousands of radiographs taken, up to 360° rotation, for an accurate volumetric reconstruction.
Because it visualises object interiors, it is the go-to technique for 3D scanning for part inspection Singapore manufacturers and engineers rely on.
Our X-ray Computed Tomography Capabilities
Our industrial CT scan Singapore facility supports a range of applications across manufacturing, aerospace, electronics, medical device and MedTech manufacturing, and more.
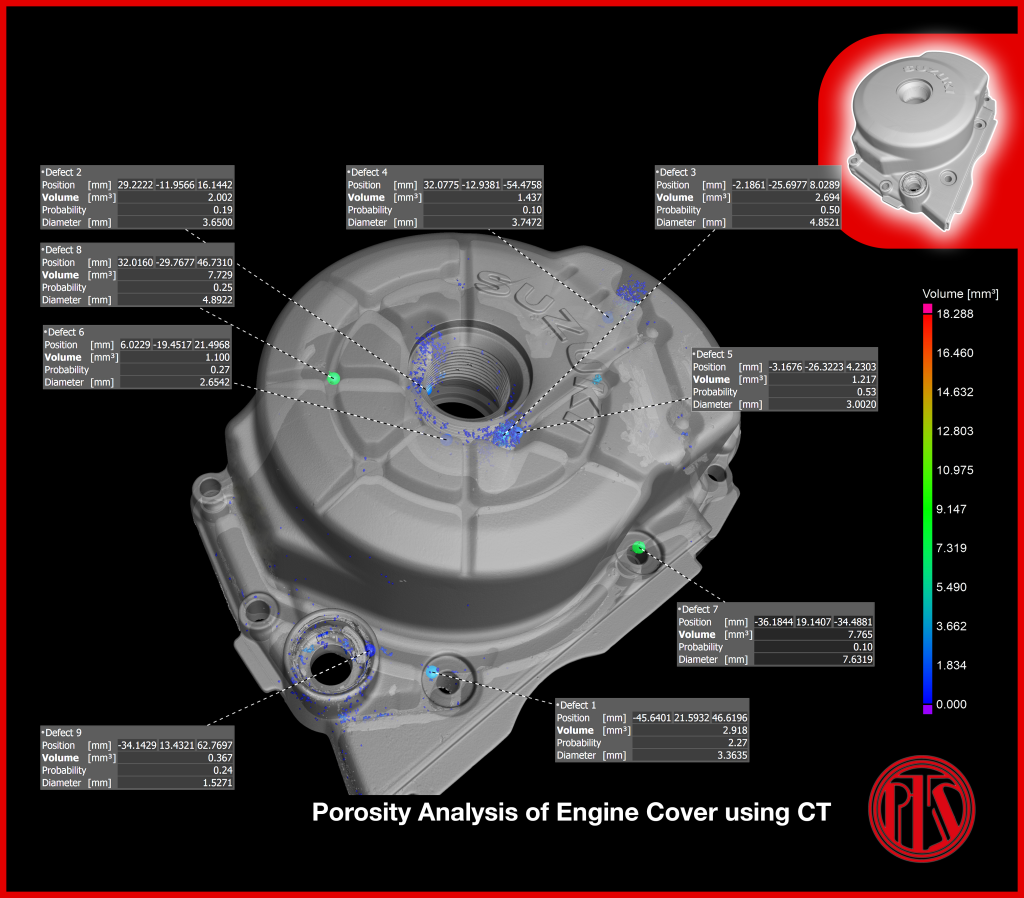
Porosity Analysis | Detect & Locate
Our 3D X-ray tomography delivers high volumetric density analysis, capable of detecting various shapes and sizes of pores.
The evaluation is carried out in 3D, precisely locating the position of every single pore. This technique can be used for:
- Product quality validation
- Casting process optimisation
- First Article Inspection
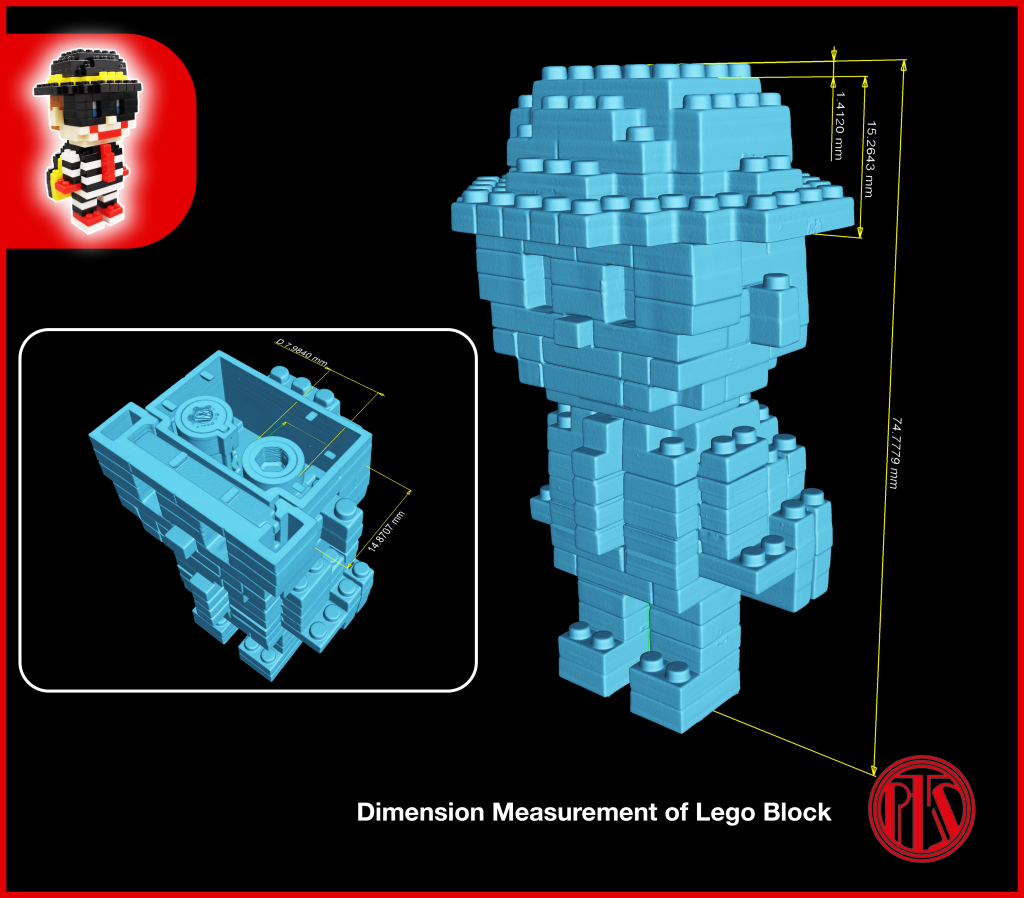
Dimensional Measurement | Fast & Accurate
Acquisition of 3D volumetric data enables simplification of complex measurements.
External and internal measurements, GD&T, and complex shapes and geometries can be easily analysed with industrial CT metrology accuracy, and specially curated for:
- First Article Inspection
- Locate and validate critical features
- Pinpoint critical defects
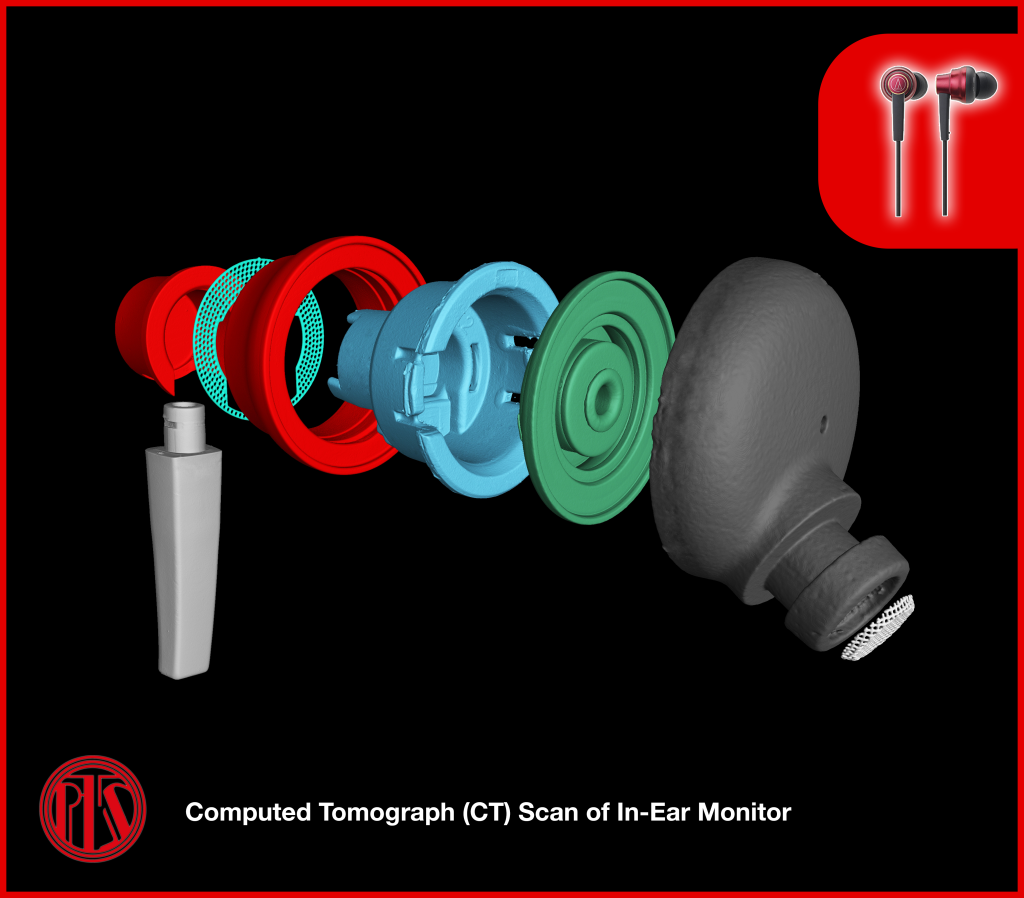
Reverse Engineering | CAD Support
X-Ray Computed Tomography features an advanced algorithm that enables existing products to be reconstructed in 3D volumetric data.
Through 3D reverse engineering services, the evaluated data can be exported in STL format, compatible with most of the CAD software for:
- Design optimisation
- Mold design correction
- Dimensional measurement
- 3D Print Prototyping

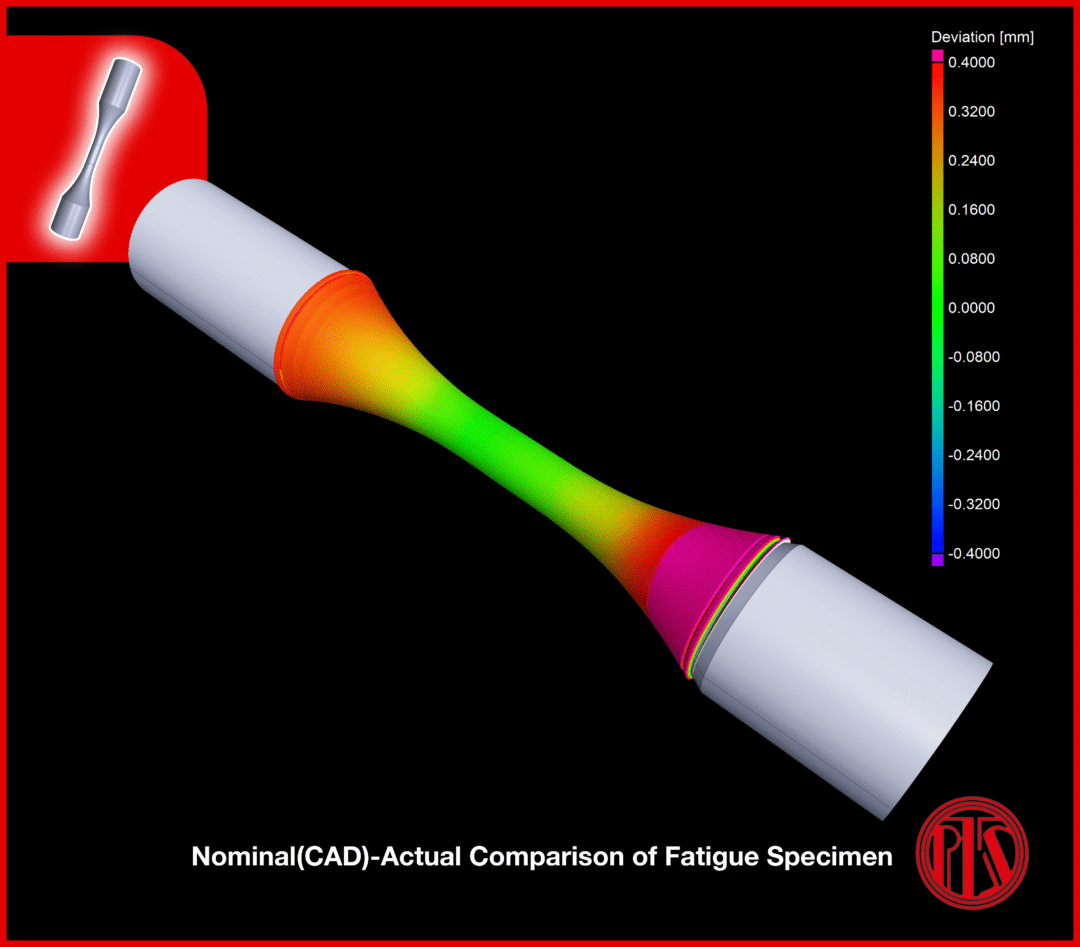
Nominal-Actual Comparison | Color Coded
High-density data from 3D X-Ray Computed Tomography enables determination of the dimensional deviation of the actual product from its nominal (CAD) design.
Colour-coded evaluation simplifies deviation analysis, especially for complex geometries and freeform surfaces. This technique can be used for:
- Overall product dimensional deviation
- Production parameter/process optimisation
- First Article Inspection
Applications of Industrial CT in Manufacturing
Uses of tomography in manufacturing continue to expand as industries demand faster, non-destructive inspection methods. Here’s where industrial CT adds the most value:
Quality Control & Defect Detection
Identify internal voids, cracks, porosity, and inclusions without destroying the part. Critical for castings, welds, and additively manufactured components.
Micro CT for Electronics Failure Analysis
Inspect solder joints, wire bonds, PCB layers, and encapsulated components. Micro CT reveals defects invisible to traditional 2D X-ray, such as voids in BGA solder balls or internal cracks in semiconductor packages.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) Validation
Verify internal lattice structures, detect trapped powder, and confirm the dimensional accuracy of printed parts before they go into service.
Metrology & Measurement
Replace coordinate measuring machines (CMM) for complex internal geometries. CT-based metrology captures features that physical probes simply can’t reach.
Reverse Engineering & Legacy Part Reproduction
Digitise existing components, even those without CAD files, for redesign, replacement, or improvement.
Common Test Methods
Our 3D scanning services Singapore laboratory operates in accordance with internationally recognised standards:
ASTM E1441
ASTM E2698
ASME V Article 20
ISO 15708
Talk to Us Today
Complimentary Test: Your first CT scan will be on us!
Professional Testing Services (PTS) is currently offering FREE trial scans of our X-ray Computed Tomography services to help engineers worldwide understand the capabilities of advanced radiography techniques and industrial CT scanning services.
All new customers are entitled to a session of free consultation and CT scan service for computed tomography in Singapore. Explore our Singapore testing services, 3D reverse engineering services Singapore, and more.
*The desired scan with the optimised parameter will be charged at the total price with an additional discount at PTS’s discretion.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How does industrial CT scanning work?
In simple terms, an X-ray source rotates around (or the part rotates within) the scanner, capturing thousands of 2D radiographic images from different angles. These images are then reconstructed into a full 3D volume using specialised software, creating a complete digital model of both external and internal features without any physical cutting or sectioning.
2. What's the difference between NDT X-ray vs computed tomography?
Traditional 2D radiography (NDT X-ray) produces flat images, which are useful for spotting defects, but are limited when features overlap. CT builds a full 3D model, so you can slice through the data in any plane and measure internal geometries with high accuracy.
3. What's the difference between Micro CT vs SEM imaging?
SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy) excels at surface detail and nanoscale resolution, but this typically requires cutting and coating the sample. Micro CT, on the other hand, is entirely non-destructive and captures internal features in 3D. For failure analysis where you need to preserve the sample or see inside without sectioning, micro CT is often the better choice.
For 2D radiographic inspection, see our Digital Radiography NDT services.
4. Is micro CT suitable for electronics failure analysis?
Yes. Micro CT is widely used for electronics failure analysis, particularly for inspecting solder joints, BGA connections, wire bonds, and encapsulated components. It reveals internal defects that a 2D X-ray might miss, such as voids, cracks, or delamination.
5. How accurate is industrial CT metrology?
Modern industrial CT systems can achieve metrology-grade accuracy, often within microns depending on part size, material density, and scan parameters. If critical dimensional verification is needed, CT can match or complement traditional CMM methods, with the added benefit of capturing internal features.









